以前にご紹介したOECD ガイドラインに沿うような年金ガバナンスとは、実際にはどういう姿になるのでしょうか。
今回は、カナダの公的年金運用組織であるCPPIB(現在の名称は CPP Investments)のガバナンス体制を見てみたいと思います。
この組織については、前にもご紹介しました。
CPPIBでのガバナンスの体制や取組内容は、年金ガバナンスのベストプラクティス例として、しばしば取り上げられます。
IMF・世界銀行・OECD などを含め世界的に広く認知されていますし、GPIFのガバナンス見直しに関する社会保障審議会年金部会等での議論の際にも、CPPIBのガバナンスモデルが度々参照されました。
下の図は CPPIBのガバナンス体制を示したものです。
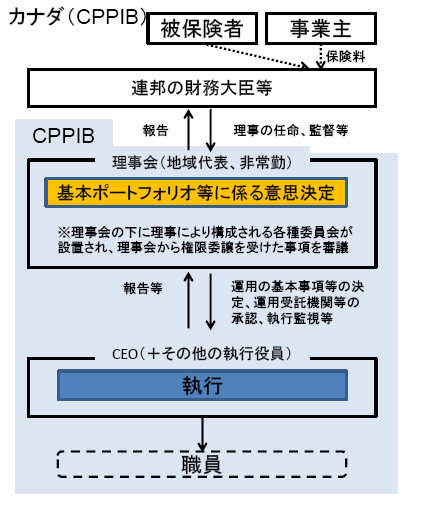
統治機関としての「理事会(the Board of Directors)」が CPPIB の運営に最終的な責任を負い、執行は CEO 以下の組織が担う体制となっています。
理事会のメンバーは 12 名で、カナダの様々な地域からの代表者から構成されています。
なお、理事は全員が非常勤です。
理事会の役割について、直近のアニュアルレポートでは次のように整理されています。
•Appoints the President & CEO and annually reviews their performance;
•Determines the organization’s strategic direction in collaboration with Management;
•Reviews and approves investment policies, standards and procedures;
•Reviews and approves the Risk Policy which establishes enterprise risk appetite;
•Approves the framework for investment transaction approvals and for retaining external investment managers;
•Reviews the Investment Portfolios and the results of investment decisions;
•Reviews and approves the annual business plan and budget;
•Oversees succession planning for Senior Management;
•Sets compensation policies and approves Senior Management compensation;
•Appoints CPP Investments’ external auditor;
•Establishes and monitors compliance with the Code of Conduct for Directors and employees;
•Establishes procedures to identify and resolve conflicts of interest;
•Establishes other policies relating to matters such as authorities, procurement, anti-corruption, privacy, and travel and expenses;
•Reviews and approves material disclosures such as quarterly and annual financial statements and the annual report; and
•Assesses the performance of the Board itself, including an annual Chairperson and Director peer review.
日本語に直してみましょう。
• CEOを任命し毎年その実績を評価する。
• 経営陣と協働して組織の戦略的方向性を決定する。
• 投資方針、基準、手続きを検討・承認する。
• 組織のリスクアペタイトを定めるリスクポリシーを検討・承認する。
• 投資取引の承認および外部マネジャーの採用に関するフレームワークを承認する。
• 投資ポートフォリオおよび投資判断の結果を振り返る。
• 年間事業計画および予算を検討・承認する。
• 経営層の後継者育成計画を監督する。
• 報酬方針を決定し、経営層の報酬を承認する。
• CPP Investments の社外監査役を選任する。
• 役職員行動基準を設定しコンプライアンス遵守状況をモニタリングする。
• 利益相反の特定および解決のための手続きを設定する。
• 権限、調達、腐敗防止、プライバシー、旅費・経費などに関する方針を定める。
• 四半期報告、年次財務諸表、アニュアルレポート等の重要な開示事項をレビューし承認する。
• 年1回の議長および理事の相互評価など、理事会自体のパフォーマンスを評価する。
理事会の役割として最初に挙げられているのは、「CEO の任命および CEO の年間実績の評価」です。
また、「戦略的方向性の決定」・「投資方針等の承認」「リスクポリシーの承認」等についても理事会の役割とされています。
つまり、基本的な方針や制約は理事会で決定し、その枠の中でCEO 以下の経営陣が執行を行う体制となっています。
このような体制とすることで、OECD の年金ガイドラインで示された「監督と執行の分離」が図られていると言えます。